Publications
Parallel simulation of inextensible cloth
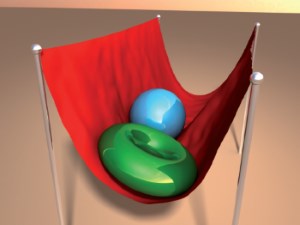
This paper presents an efficient simulation method for parallel cloth simulation. The presented method uses an impulse-based approach for the simulation. Cloth simulation has many application areas like computer animation, computer games or virtual reality. Simulation methods often make the assumption that cloth is an elastic material. In this way the simulation can be performed very efficiently by using spring forces. These methods disregard the fact that many textiles cannot be stretched significantly. The simulation of inextensible textiles with methods based on spring forces leads to stiff differential equations which cause a loss of performance. In contrast to that, in this paper a method is presented that simulates cloth by using impulses. The mesh of a cloth model is subdivided into strips of constraints. The impulses for each strip can be computed in linear time. The strips that have no common particle are independent from each other and can be solved in parallel. The impulse-based method allows the realistic simulation of inextensible textiles in real-time.
@inproceedings{Bender08,
author = {Jan Bender and Daniel Bayer},
title = {Parallel simulation of inextensible cloth},
booktitle = {Virtual Reality Interactions and Physical Simulations (VRIPhys)},
year = {2008},
month = nov,
address = {Grenoble (France)},
pages = {47-56}
}
Semantic representation of complex building structures

In this paper we present an abstract semantic representation that is suitable for complex buildings. Facades with high-level detail are required in several domains, e.g. visualization of architectural settings and archaeological sites as well as computer animations. In order to support the user’s modeling task, besides geometrical data structural information like spatial relations is required. This supplementary information represents the semantics of the model. Therefore the model description must incorporate the geometry and the semantics. Such a description allows a partial automation of the modeling process, e.g. adjacent and nested elements are adjusted automatically. An abstract model representation with integrated semantics is presented in this paper and it is shown that it facilitates the modeling task significantly.
@inproceedings{Finkenzeller08,
author = {Dieter Finkenzeller and Jan Bender},
title = {Semantic representation of complex building structures},
booktitle = {Computer Graphics and Visualization (CGV 2008) - IADIS Multi Conference on Computer Science and Information Systems},
year = {2008},
month = jul,
address = {Amsterdam (Netherlands)}
}
Impulse-based simulation of inextensible cloth
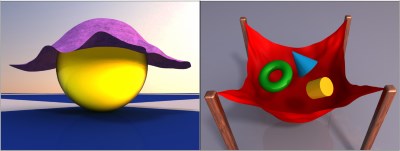
In this paper an impulse-based method for cloth simulation is presented. The simulation of cloth is required in different application areas like computer animation, virtual reality or computer games. Simulation methods often assume that cloth is an elastic material. With this assumption the simulation can be performed very efficiently using spring forces. The problem is that many textiles cannot be stretched significantly. A realistic simulation of these textiles with spring forces leads to stiff differential equations which cause a deterioration of performance. The impulse-based method described in this paper solves this problem and allows the realistic simulation of inelastic textiles.
@inproceedings{Bender08,
author = {Jan Bender and Daniel Bayer},
title = {Impulse-based simulation of inextensible cloth},
booktitle = {Computer Graphics and Visualization (CGV 2008) - IADIS Multi Conference on Computer Science and Information Systems},
year = {2008},
month = jul,
address = {Amsterdam (Netherlands)}
}
Impulsbasierte Dynamiksimulation von Mehrkörpersystemen in der virtuellen Realität
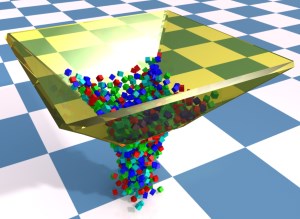
Die dynamische Simulation gewinnt im Bereich der virtuellen Realität immer mehr an Bedeutung. Sie ist ein wichtiges Hilfsmittel, um den Grad der Immersion des Benutzers in eine virtuelle Welt zu erhöhen. In diesem Anwendungsbereich ist die Geschwindigkeit des verwendeten Simulationsverfahrens entscheidend. Weitere Anforderungen an das Verfahren sind unter anderem Genauigkeit, Stabilität und eine einfache Implementierung. In dieser Arbeit wird ein neues impulsbasiertes Verfahren für die dynamische Simulation von Mehrkörpersystemen vorgestellt. Dieses erfüllt, im Gegensatz zu klassischen Verfahren, alle Anforderungen der virtuellen Realität. Das vorgestellte Verfahren arbeitet ausschließlich mit Impulsen, um mechanische Gelenke, Kollisionen und bleibende Kontakte mit Reibung zu simulieren.
@inproceedings{Bender08,
author = {Jan Bender},
title = {Impulsbasierte Dynamiksimulation von Mehrkörpersystemen in der virtuellen Realität},
booktitle = {GI-Edition Lecture Notes in Informatics (LNI) - Ausgezeichnete Informatikdissertationen 2007},
year = {2008},
pages = {21-30}
}
Vergleich der impulsbasierten Dynamiksimulation mit der Lagrange-Faktoren-Methode
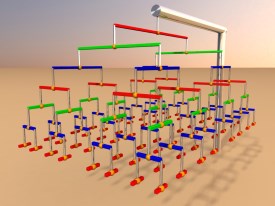
Eine der am weitesten verbreiteten Methoden zur Simulation von mechanischen Starrkörpersystemen ist die Lagrange-Faktoren-Methode (LFM). Die impulsbasierte Dynamiksimulation ist ein neuer alternativer Ansatz zur Simulation solcher Systeme. Durch den direkten Vergleich werden in dieser Arbeit die Vor- und Nachteile der beiden Methoden aufgezeigt. Dazu wird neben einer Laufzeit- und Genauigkeitsmessung zusätzlich ein informeller Vergleich durchgeführt und die Ergebnisse diskutiert.
@inproceedings{Bayer08,
author = {Daniel Bayer and Jan Bender},
title = {Vergleich der impulsbasierten Dynamiksimulation mit der Lagrange-Faktoren-Methode},
booktitle = {5. Workshop "Virtuelle und Erweiterte Realität der Fachgruppe VR/AR"},
year = {2008},
month = sep,
address = {Magdeburg (Germany)},
pages = {185-196}
}
Design of a dynamic simulation system for VR applications
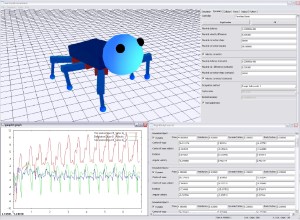
A dynamic simulation system for VR applications consists of multiple parts. The first task that must be accomplished is the generation of complex dynamic models. A 3D modelling tool is required that supports the definition of joint constraints and dynamic parameters. For the dynamic simulation of the generated models a modular simulator is required. This simulator must handle constrained models, detect and resolve collisions regarding dynamic and static friction, manage user interactions and provide the possibility of extensions. It also requires an interface for the output of the simulation data. There exist several different methods for the dynamic simulation of joint constraints, for collision detection and for the handling of collisions and resting contacts with friction. The simulation system should support multiple of these methods and provide the possibility to exchange them at runtime.
@TechReport{Bender08_13,
author = "Jan Bender",
title = "Design of a dynamic simulation system for VR applications",
institution = "University of Karlsruhe",
year = "2008",
type = "Technical Report",
number = "13"
}
Previous Year (2007)

