Turbulent Micropolar SPH Fluids with Foam
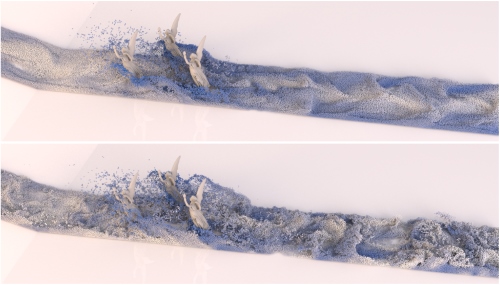
In this paper we introduce a novel micropolar material model for the simulation of turbulent inviscid fluids. The governing equations are solved by using the concept of Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH). As already investigated in previous works, SPH fluid simulations suffer from numerical diffusion which leads to a lower vorticity, a loss in turbulent details and finally in less realistic results. To solve this problem we propose a micropolar fluid model. The micropolar fluid model is a generalization of the classical Navier-Stokes equations, which are typically used in computer graphics to simulate fluids. In contrast to the classical Navier-Stokes model, micropolar fluids have a microstructure and therefore consider the rotational motion of fluid particles. In addition to the linear velocity field these fluids also have a field of microrotation which represents existing vortices and provides a source for new ones. However, classical micropolar materials are viscous and the translational and the rotational motion are coupled in a dissipative way. Since our goal is to simulate turbulent fluids, we introduce a novel modified micropolar material for inviscid fluids with a non-dissipative coupling. Our model can generate realistic turbulences, is linear and angular momentum conserving, can be easily integrated in existing SPH simulation methods and its computational overhead is negligible. Another important visual feature of turbulent liquids is foam. Therefore, we present a post-processing method which considers microrotation in the foam particle generation. It works completely automatic and requires only one user-defined parameter to control the amount of foam.
@Article{BKKW19,
author = {Bender, Jan and Koschier, Dan and Kugelstadt, Tassilo and Weiler, Marcel},
title = {Turbulent Micropolar SPH Fluids with Foam},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics},
year = {2019},
publisher = {IEEE},
volume={25},
number={6},
pages={2284-2295},
doi={10.1109/TVCG.2018.2832080},
ISSN={1077-2626},
month={June},
}

